Specify Delimiter when Reading pandas DataFrame from CSV File in Python (Example)
In this article you’ll learn how to change the separator when importing a pandas DataFrame from a CSV file in Python.
The tutorial will contain these content blocks:
Here’s how to do it…
Example Data & Software Libraries
First, we need to import the pandas library:
import pandas as pd # Import pandas library in Python
As a next step, let’s also create some example data in Python:
data = pd.DataFrame({'x1':range(1, 8), # Create pandas DataFrame 'x2':['x', 'y', 'y', 'z', 'z', 'y', 'z'], 'x3':range(18, 11, - 1), 'x4':['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g']})
We can now write this pandas DataFrame to a CSV file using the to_csv function:
data.to_csv('data.csv', # Export pandas DataFrame to CSV index = False, sep = ';')
If we would now load this CSV file into Python with the default separator specifications of the read_csv function, the output would look as shown below:
data_import_default = pd.read_csv('data.csv') # Import CSV file print(data_import_default) # Print imported CSV file # x1;x2;x3;x4 # 0 1;x;18;a # 1 2;y;17;b # 2 3;y;16;c # 3 4;z;15;d # 4 5;z;14;e # 5 6;y;13;f # 6 7;z;12;g
As you can see, our imported pandas DataFrame is not shown properly. Let’s fix this!
Example: Specify Separator when Importing a pandas DataFrame from a CSV File
This example shows how to set an appropriate delimiter when reading a CSV file as pandas DataFrame to Python.
For this task, we can use the sep argument as shown below. In this specific case, we are using a semicolon instead of a comma as separator:
data_import_sep = pd.read_csv('data.csv', # Import CSV file sep = ';') print(data_import_sep) # Print imported CSV file
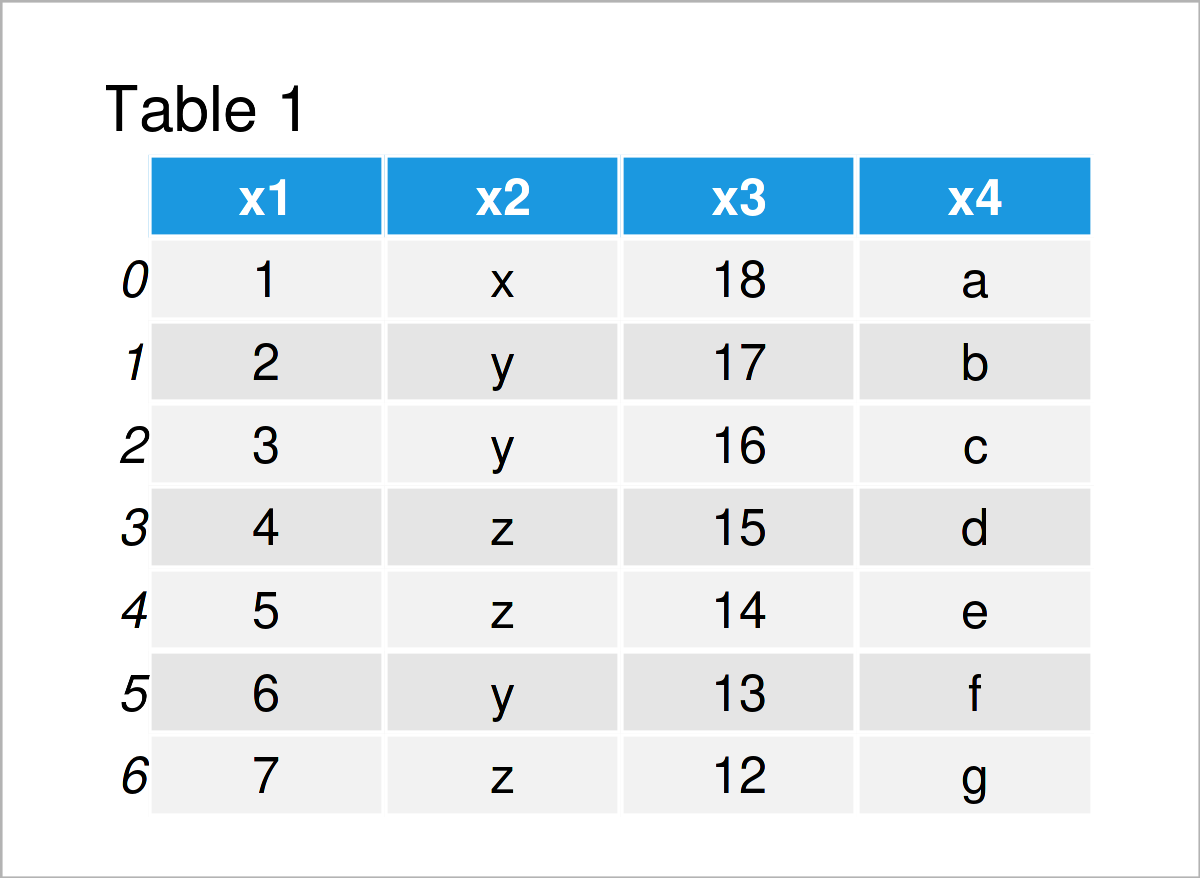
Table 1 shows the structure of our example data: It contains seven rows and four variables. As you can see, it has been imported properly.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
Some time ago, I have published a video on my YouTube channel, which demonstrates the topics of this article. You can find the video below:
The YouTube video will be added soon.
Furthermore, you may read some of the related Python articles on this homepage:
- pandas Library Tutorial in Python
- Specify dtype when Reading pandas DataFrame from CSV File
- Read Multiple CSV Files & Append into One pandas DataFrame
- Read CSV File Line by Line in Python
- Ignore Header when Reading CSV File as pandas DataFrame
- Read CSV File as pandas DataFrame in Python
- DataFrame Manipulation Using pandas in Python
- Drop First & Last N Columns from pandas DataFrame in Python
- Get Values of First Row in pandas DataFrame in Python
- Insert Column at Specific Position of pandas DataFrame in Python
- Introduction to Python Programming
To summarize: In this tutorial you have learned how to use a different delimiter when importing a pandas DataFrame from a CSV file in Python. Please tell me about it in the comments, in case you have further questions.







2 Comments. Leave new
Thank you very much for this topic!
When I change the separator type to ‘\t’ or ‘=’ it does not work. Does the semicolon always stay by default? How can I change it?
Hello,
It should also work with other separators. See the implementation below.
If you still struggle, I will let one of our authors, who is more experienced in python, know.
Regards,
Cansu