Write pandas DataFrame to CSV File in Python (4 Examples)
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to export a pandas DataFrame as a CSV file in the Python programming language.
The article contains the following content:
If you want to know more about these topics, keep reading.
Example Data & Add-On Libraries
If we want to use the functions of the pandas library, we first need to import pandas:
import pandas as pd # Import pandas library in Python
The data below is used as a basis for this Python programming language tutorial:
data = pd.DataFrame({'x1':range(1, 7), # Create pandas DataFrame 'x2':[3, 9, 7, 3, 1, 8], 'x3':['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'], 'x4':range(15, 9, - 1)}) print(data) # Print pandas DataFrame
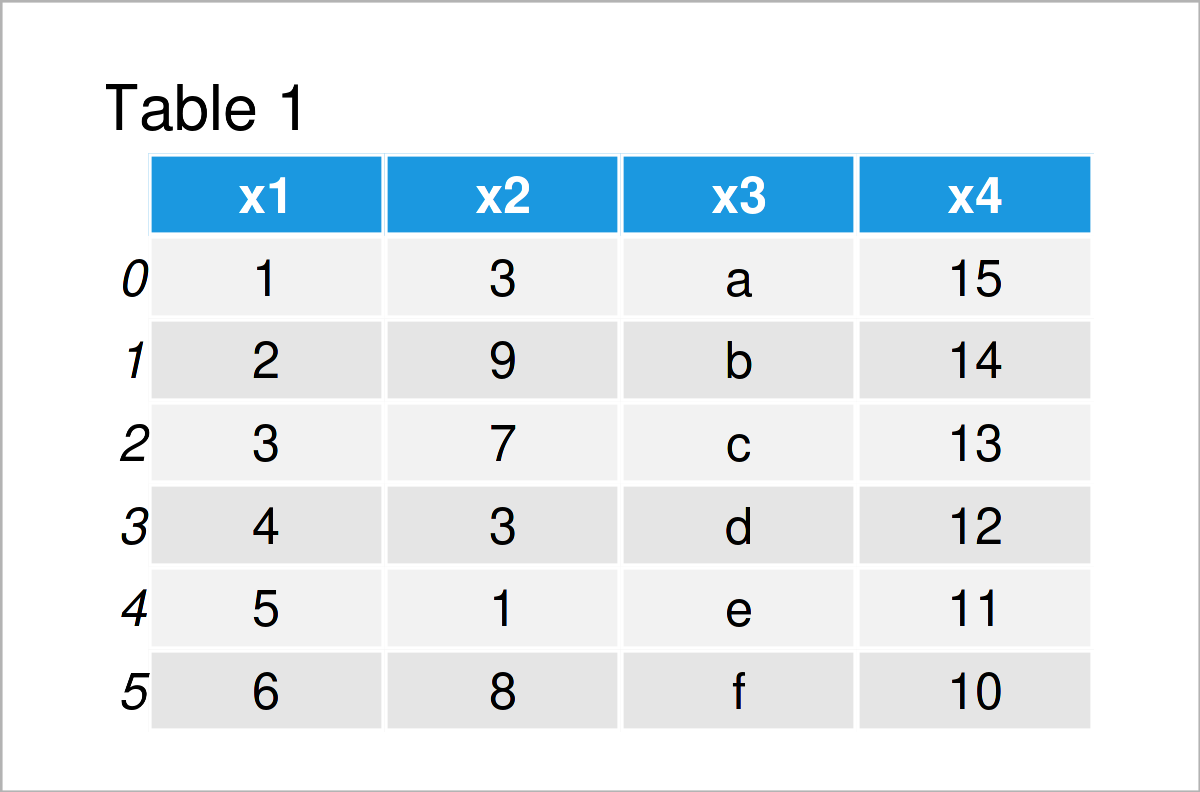
The previously shown table illustrates the output of the Python console and shows that the example pandas DataFrame has six observations and four variables.
In case we want to write our data to a specific folder, we also have to set this folder as our working directory.
For this, we first have to import the os module:
import os # Load os
Next, we can set our working directory as shown below:
os.chdir('C:/Users/Joach/Desktop/my directory') # Set working directory
We are fully prepared now. Let’s create some CSV outputs!
Example 1: Save pandas DataFrame as CSV File Using Default Settings
This section shows the most basic way on how to save a pandas DataFrame to a CSV file.
For this task, we can apply the to_csv function as shown below. All we have to specify is the name of our data set (i.e. data) and the name of the CSV file that we want to create (i.e. data.csv).
Let’s do this:
data.to_csv('data1.csv') # Export pandas DataFrame
After executing the previous Python code, we can find a new CSV file in our working directory that looks as shown in the following screenshot:
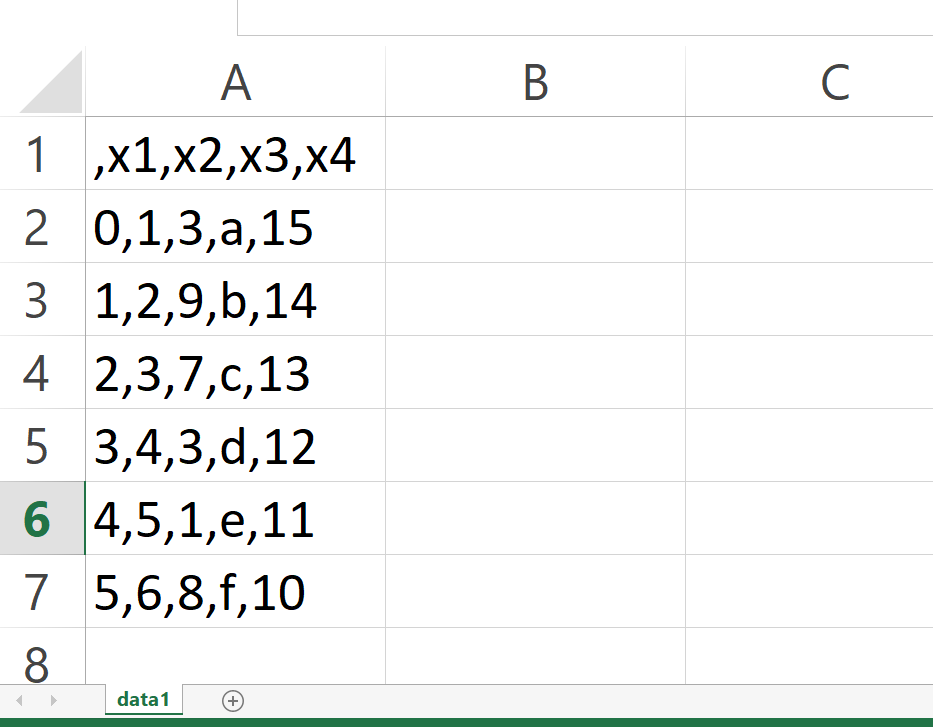
As you can see, we have managed to create a CSV file containing the header, columns, and rows of our pandas DataFrame.
However, you can also see that our data is shown with a comma separator in only one column of the CSV file. Let’s change this!
Example 2: Save pandas DataFrame as CSV File with Different Separator
The following syntax illustrates how to switch the separator of the output CSV.
To accomplish this, we have to specify the sep argument as shown below. In this specific example, we’ll use a semicolon as separator:
data.to_csv('data2.csv', # Export pandas DataFrame sep = ";")
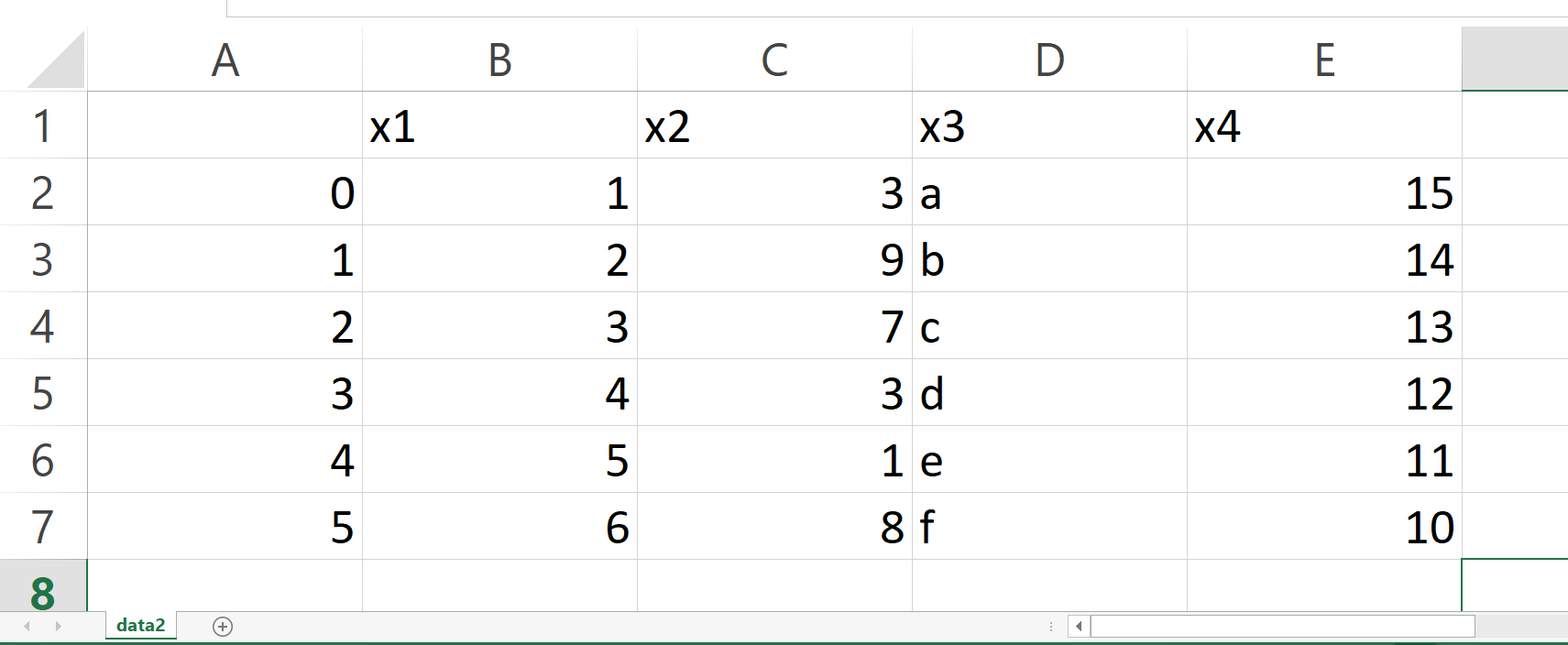
The previous Python syntax has saved another CSV file to our working directory, which contains our pandas DataFrame with a semicolon-separator in multiple columns:
Example 3: Save pandas DataFrame as CSV File without Index
In Example 3, I’ll explain how to download a pandas DataFrame from Python to a CSV file without showing the index numbers in the final output.
For this task, we have to set the index argument to be equal to False, as you can see in the following Python code:
data.to_csv('data3.csv', # Export pandas DataFrame sep = ";", index = False)
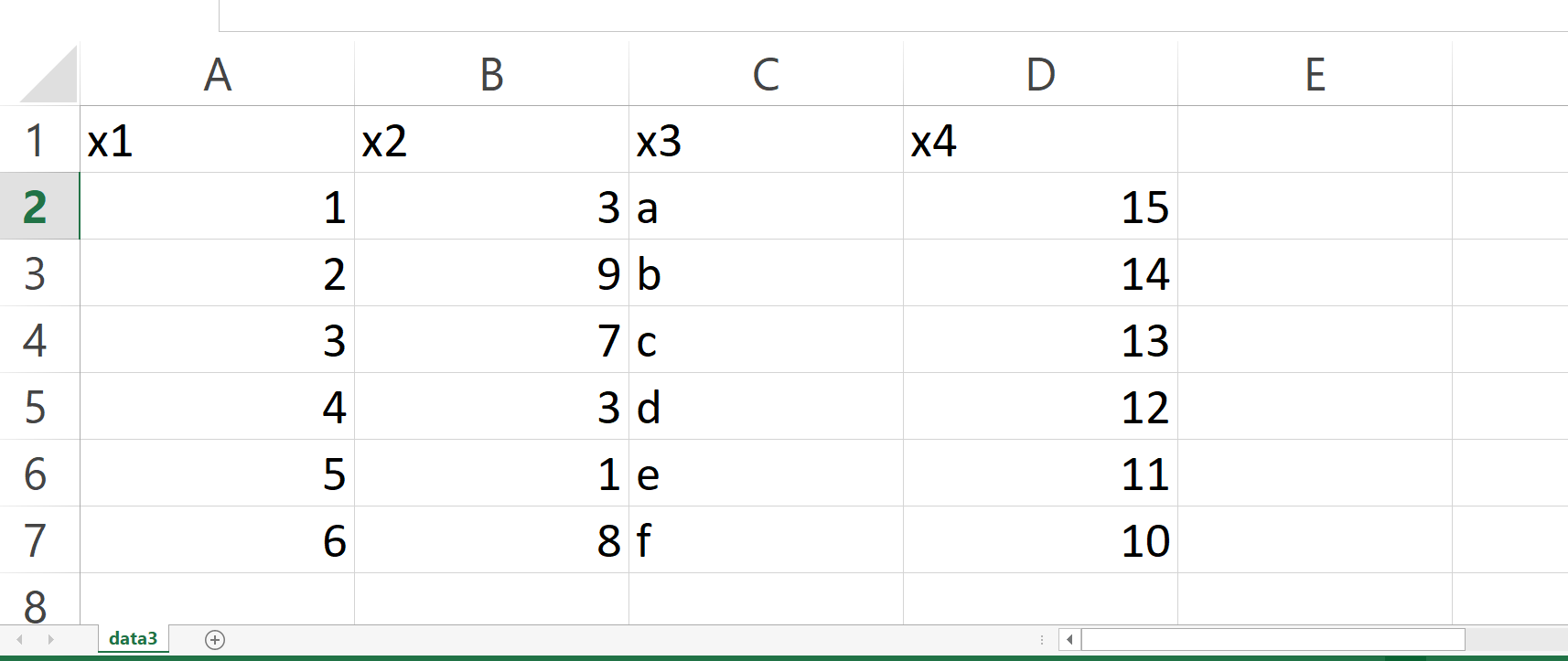
After running the code above, the CSV file shown below is appearing in our working directory:
Example 4: Append New Column to pandas DataFrame in CSV File
Until now, we have created entirely new CSV files. In Example 4, in contrast, I’ll demonstrate how to add a column to an already existing CSV file.
Let’s first create a new list object that we will append as a new column later on. Note that this list needs to have the same length as the number of rows in our CSV file.
new_col = ['foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'foo', 'bar', 'foo'] # Create list object print(new_col) # Print list object # ['foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'foo', 'bar', 'foo']
Next, we can read an already existing CSV file to which we want to add our list as another variable into Python. In this example, we’ll load the CSV file that we have constructed in the previous example:
data4 = pd.read_csv('data3.csv', # Read CSV file sep = ";")
Next, we can add our list as a new variable to our imported pandas DataFrame:
data4['new_col'] = new_col # Add list as new column
In the next step, we can convert this updated pandas DataFrame to another CSV file as shown below:
data4.to_csv('data4.csv', # Export pandas DataFrame sep = ";", index = False)
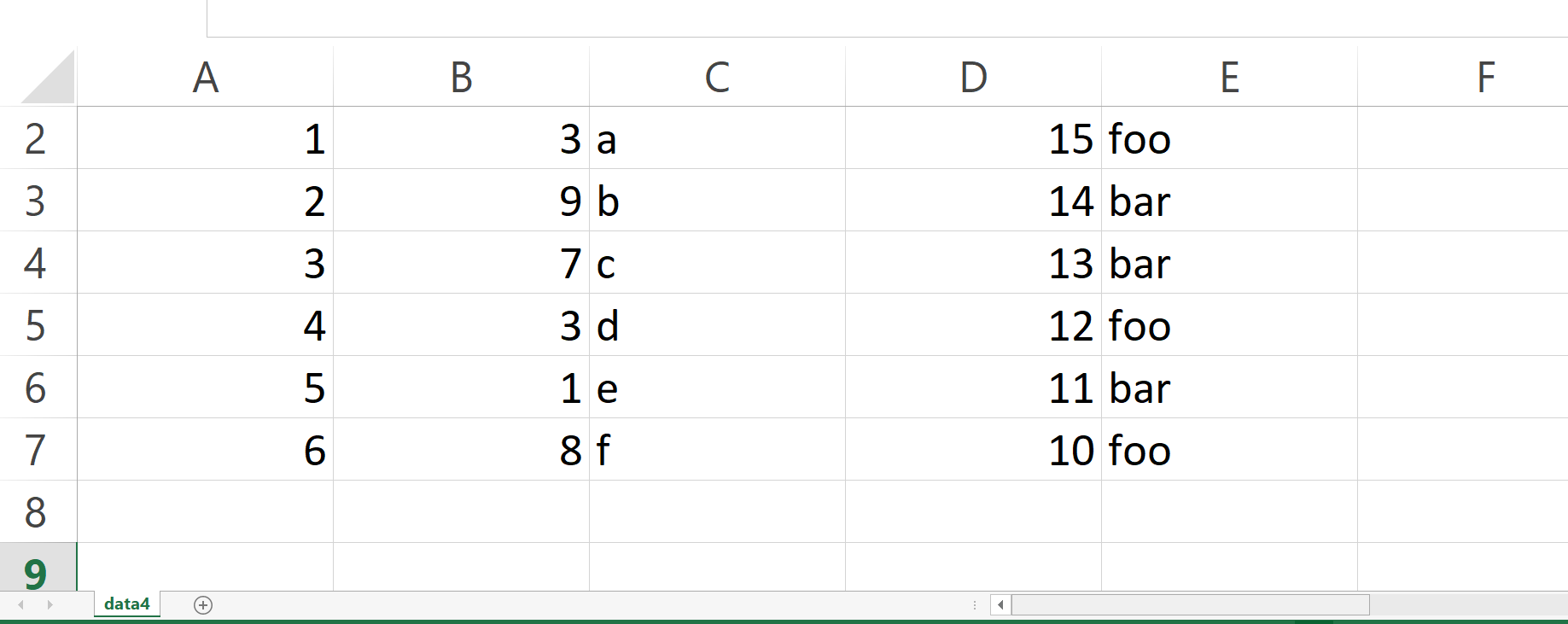
The table below shows our final output file, i.e. a CSV file with an additional column:
Video, Further Resources & Summary
Have a look at the following video on my YouTube channel. In the video, I illustrate the examples of this article in a live session:
The YouTube video will be added soon.
Furthermore, you may want to read the related tutorials on my homepage.
- pandas Library Tutorial in Python
- Write pandas DataFrame to CSV File without Index
- Write pandas DataFrame to CSV File with & without Header
- Add New Column to Existing CSV File in Python
- Append pandas DataFrame to Existing CSV File
- Merge pandas DataFrames in CSV Files in Python
- Set Column Order when Writing pandas DataFrame to CSV
- Write Multiple CSV Files in Python
- Read CSV File as pandas DataFrame in Python
- Add Column from Another pandas DataFrame in Python
- Access Index of Last Element in pandas DataFrame in Python
- Slice pandas DataFrame by Index in Python
- Append Values to pandas DataFrame in Python
- The Python Programming Language
Summary: In this tutorial, I have shown how to convert, save, and print a pandas DataFrame as a CSV file in the Python programming language. If you have additional comments and/or questions, let me know in the comments below. Furthermore, please subscribe to my email newsletter to receive updates on new articles.






