Find Common Rows Between Two Data Frames in R (2 Examples)
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to return all rows that exist in two data frames in the R programming language.
The article will contain these contents:
Let’s take a look at some R codes in action:
Creating Example Data
The data below will be used as basement for this R tutorial:
data1 <- data.frame(x1 = 1:5, # Create first example data x2 = letters[1:5], x3 = "x") data1 # Print first example data
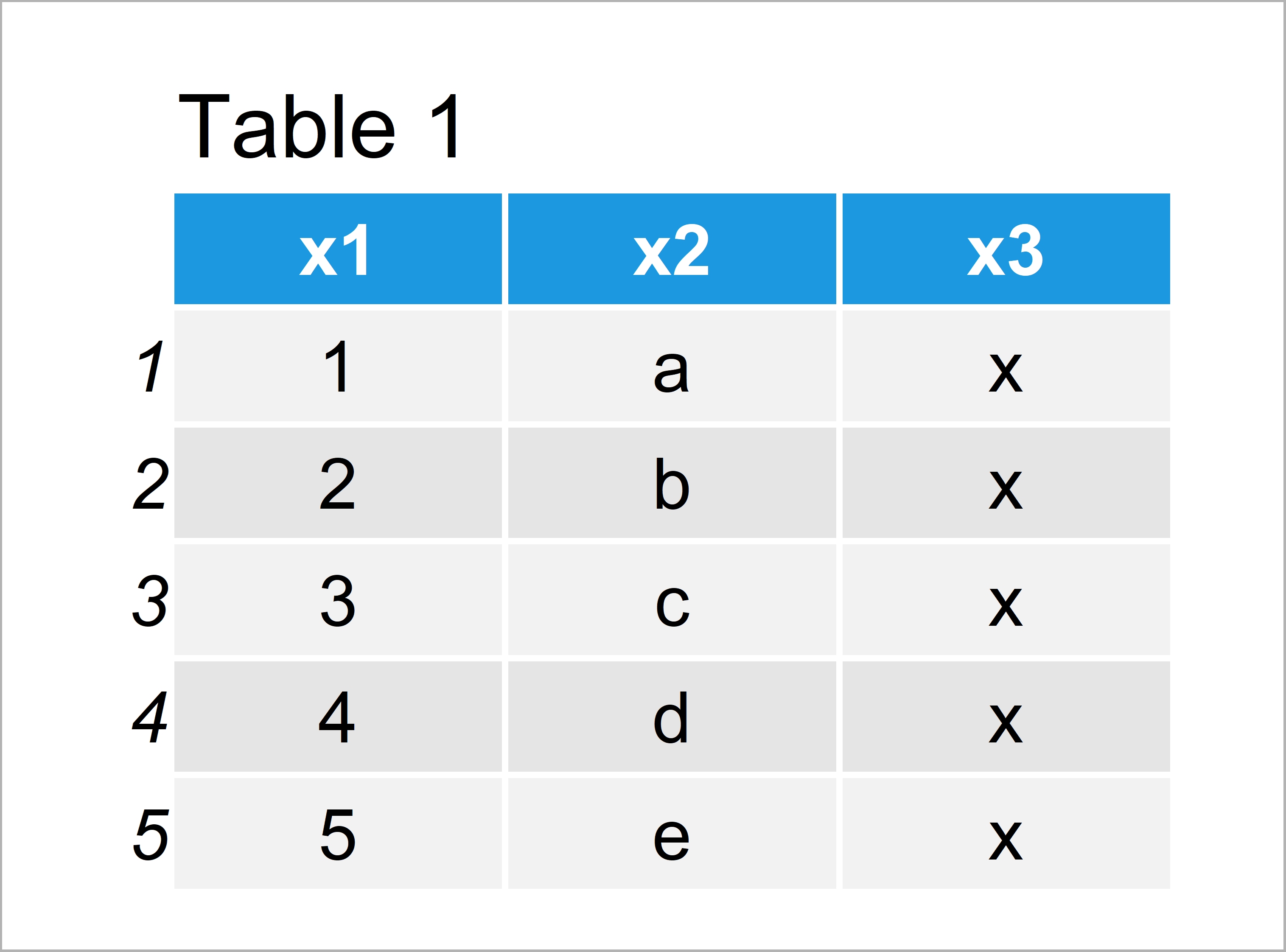
As you can see based on Table 1, our first example data is a data frame having five data points and three variables.
Let’s create a second data frame that we can compare with our first data frame:
data2 <- data.frame(x1 = 3:6, # Create second example data x2 = letters[3:6], x3 = c("x", "x", "y", "y")) data2 # Print second example data
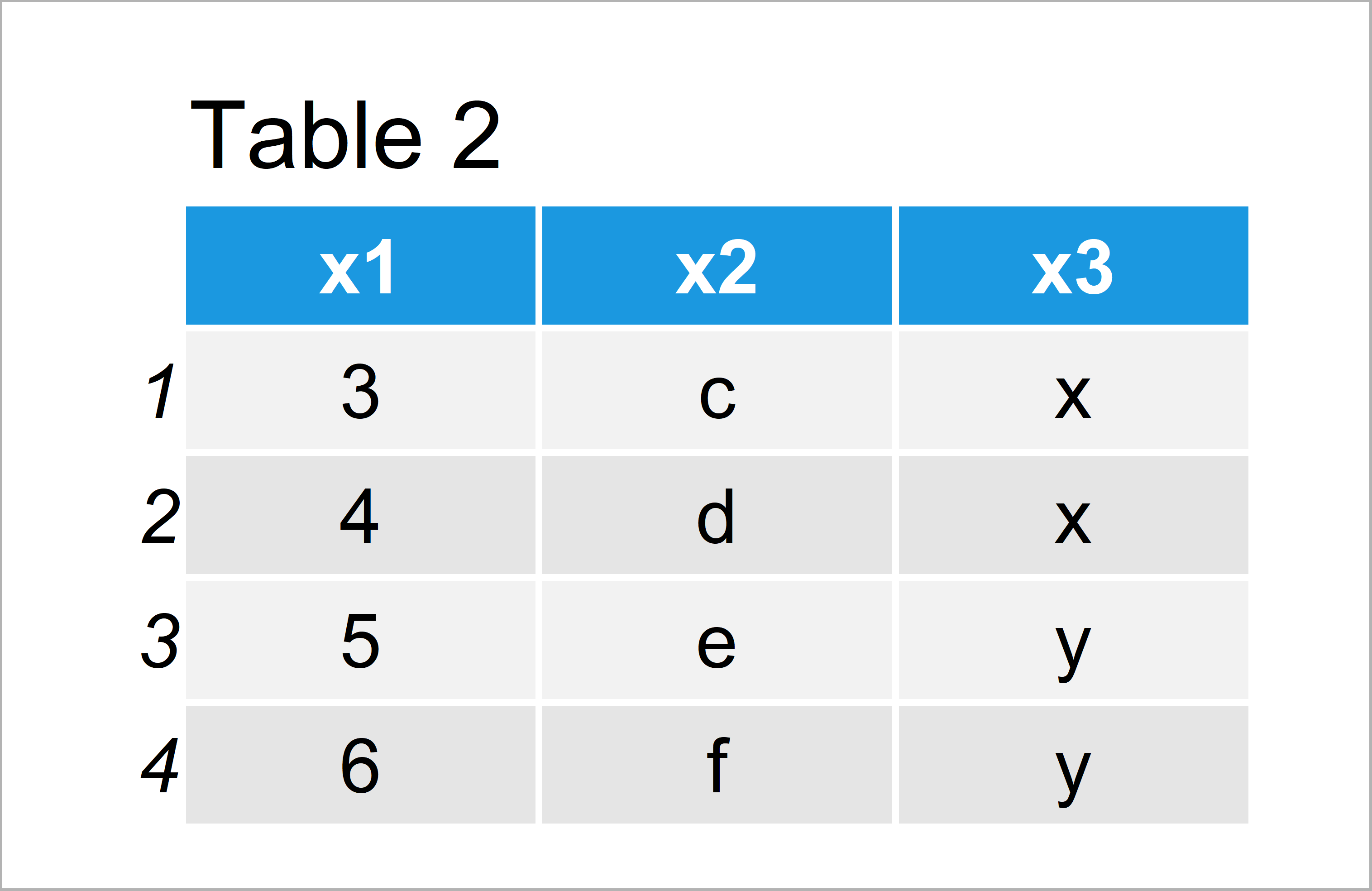
As shown in Table 2, the previous R syntax has created another data frame object consisting of four rows and the same three variables as data1.
Example 1: Identify Common Rows Between Two Data Frames Using intersect() Function of generics Package
Example 1 illustrates how to find shared rows of two data frames using the intersect function of the generics package.
Note that the generics package is already loaded with the basic installation of the R programming language. However, it is important to specify the package explicitly, since other R packages also contain functions with the name “intersect”.
Have a look at the following R code:
data_common1 <- generics::intersect(data1, data2) # Apply intersect function data_common1 # Print common data
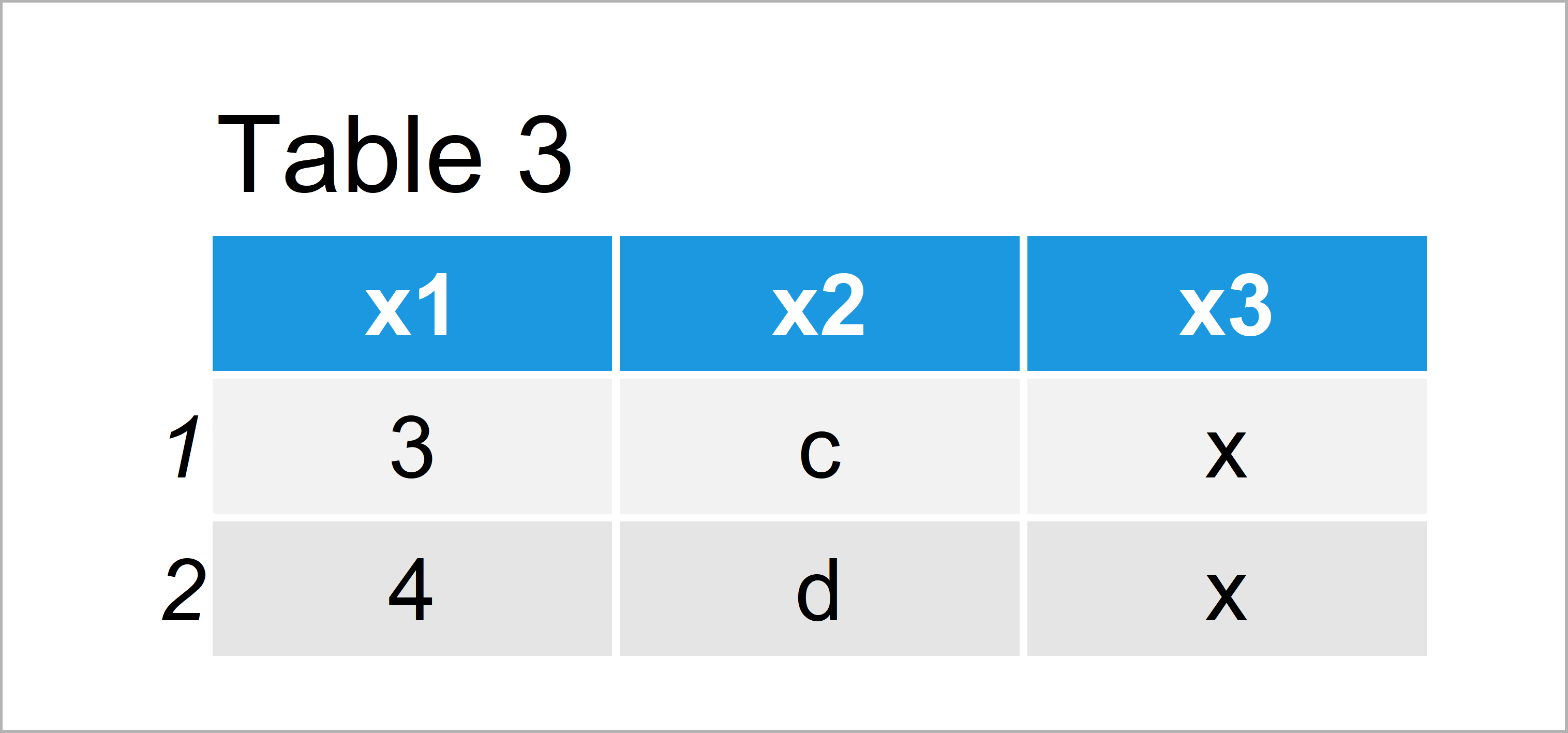
As shown in Table 3, the previous R code has created a new data frame containing only the rows that both input data frames have in common.
Example 2: Identify Common Rows Between Two Data Frames Using inner_join() Function of dplyr Package
The following syntax explains how to find duplicate rows in two data frames using the inner_join function of the dplyr add-on package.
In order to apply the functions of the dplyr package, we first need to install and load dplyr:
install.packages("dplyr") # Install & load dplyr package library("dplyr")
Next, we can apply the inner_join function like this:
data_common2 <- inner_join(data1, data2) # Apply inner_join function data_common2 # Print common data
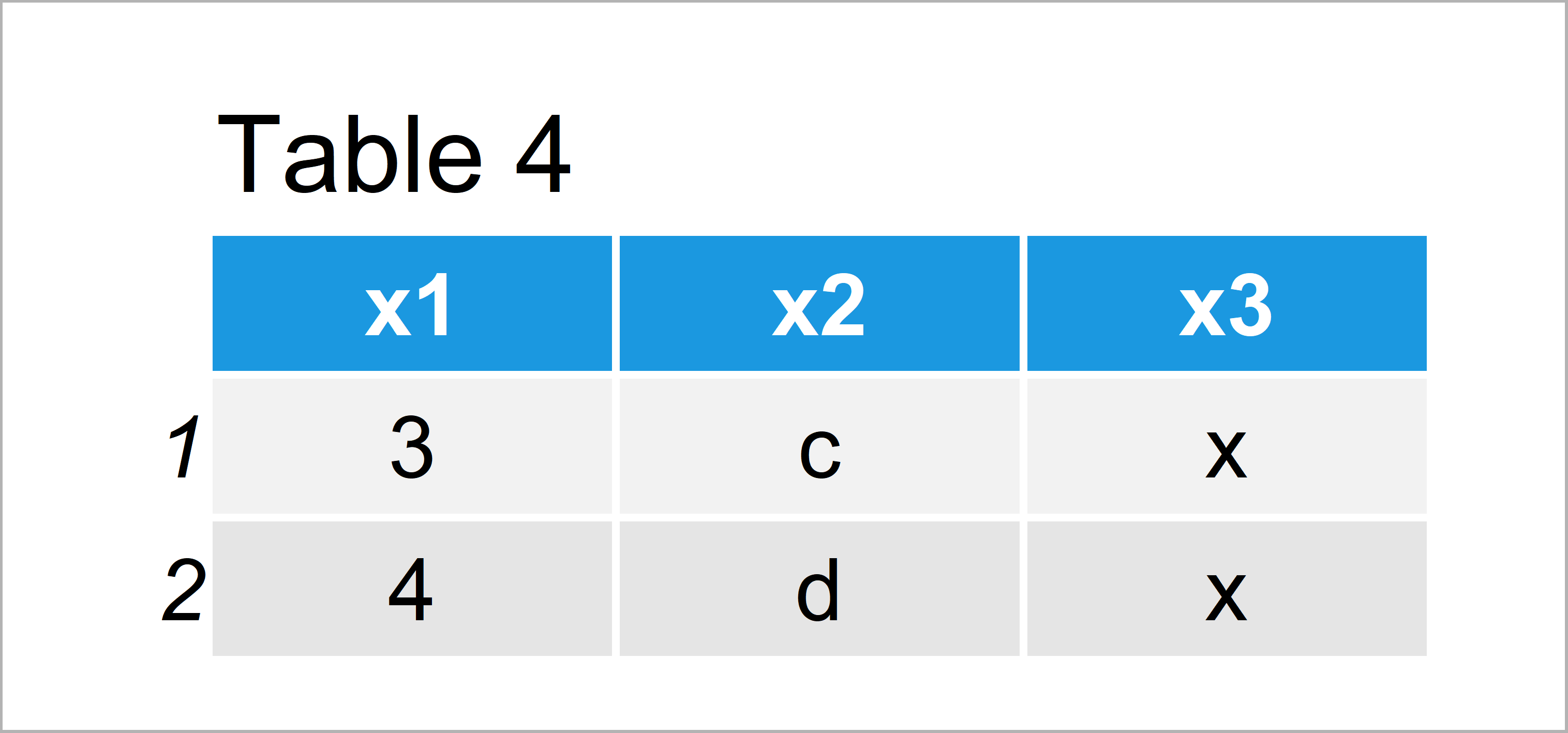
In Table 4 it is shown that we have constructed the same data frame as in the previous example. Whether you prefer to use the intersect function or the inner_join function is a matter of taste.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
In case you need further information on the examples of this tutorial, I recommend watching the following video of my YouTube channel. I explain the R programming syntax of this page in the video.
In addition, you may have a look at the other articles of this website:
- Combine Two ggplot2 Plots from Different Data Frames
- Merge Data Frames by Two ID Columns
- Find Rows in First Data Frame that are not in Second
- Merge Two Unequal Data Frames & Replace NA with 0
- union Function in R
- Combine Two Data Frames with Different Variables by Rows
- All R Programming Tutorials
In this article you have learned how to identify rows that are duplicated in two data frames in R programming. In case you have any additional questions, please let me know in the comments section below.







2 Comments. Leave new
The example you show in this article legitimately doesn’t work for me. Not sure if there has been updates to generics package or something but I figured I would mention it.
Hello Tanner,
What kind of error do you get when you run the code? Could you share the exact error here?
Regards,
Cansu