cbind R Command | 3 Example Codes (Data Frame, Vector & Multiple Columns)
Basic R Syntax:
cbind(my_data, new_column)
The name of the cbind R function stands for column-bind. The cbind function is used to combine vectors, matrices and/or data frames by columns. The code above, illustrates the basic syntax for cbind in R.
In the following article, I will show 3 examples for the usage of the cbind R command. If you want to know more about the cbind R function, keep reading.
Example 1: cbind Vector to Data Frame
A popular way of using the cbind command in the R programming language is the combination of a vector and a data.frame. Before we can start with the first cbind example, let’s create an example data frame…
data_1 <- data.frame(x1 = c(7, 3, 2, 9, 0), # Column 1 of data frame x2 = c(4, 4, 1, 1, 8), # Column 2 of data frame x3 = c(5, 3, 9, 2, 4)) # Column 3 of data frame
…and an example vector / column:
y1 <- c(9, 8, 7, 6, 5) # Create vector
Now, we can cbind this vector as a new column to our example data frame:
data_new1 <- cbind(data_1, y1) # cbind vector to data frame data_new1 # Print data to RStudio console
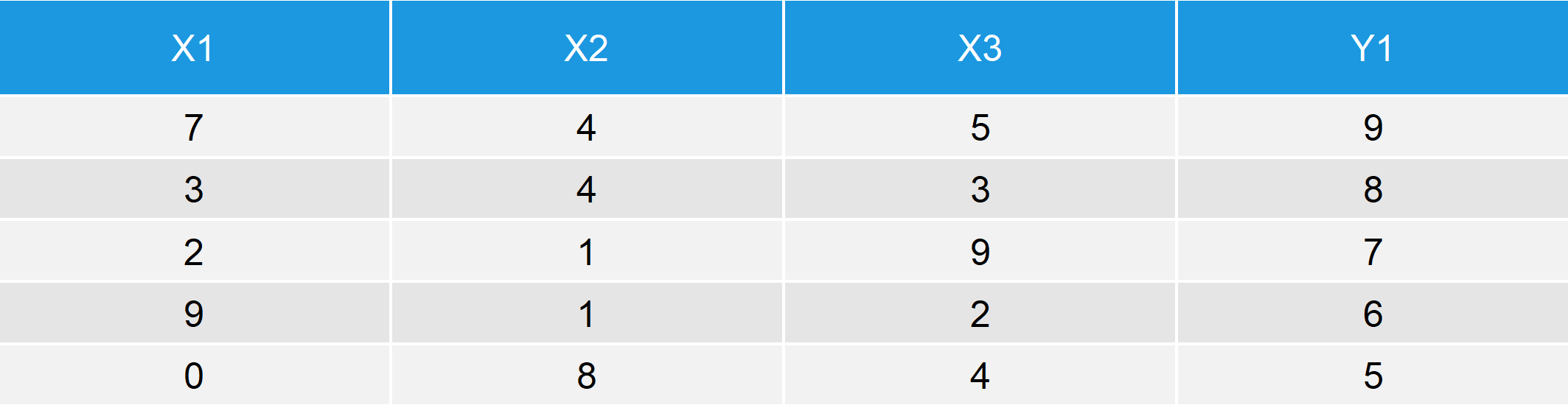
Table 1: New Data Table after Column Binding a Vector to a Data Frame.
Table 1 illustrates the RStudio output of the cbind command: The first three columns of our new data matrix are identical to our original data frame data_1 and the fourth column is identical to the vector Y1.
Example 2: cbind Two Data Frames in R Programming
The cbind command can be applied to two data frames in the same manner. First, let’s create a second data frame and cbind it to data_1 (the data table that we already used in Example 1):
data_2 <- data.frame(z1 = c(1, 5, 9, 4, 0), # Column 1 of data frame 2 z2 = c(0, 9, 8, 1, 6)) # Column 2 of data frame 2
Now, let’s column bind these two data frames. We can use basically the same R code as in the cbind Example 1:
data_new2 <- cbind(data_1, data_2) # cbind two data frames in R data_new2 # Print data to RStudio console
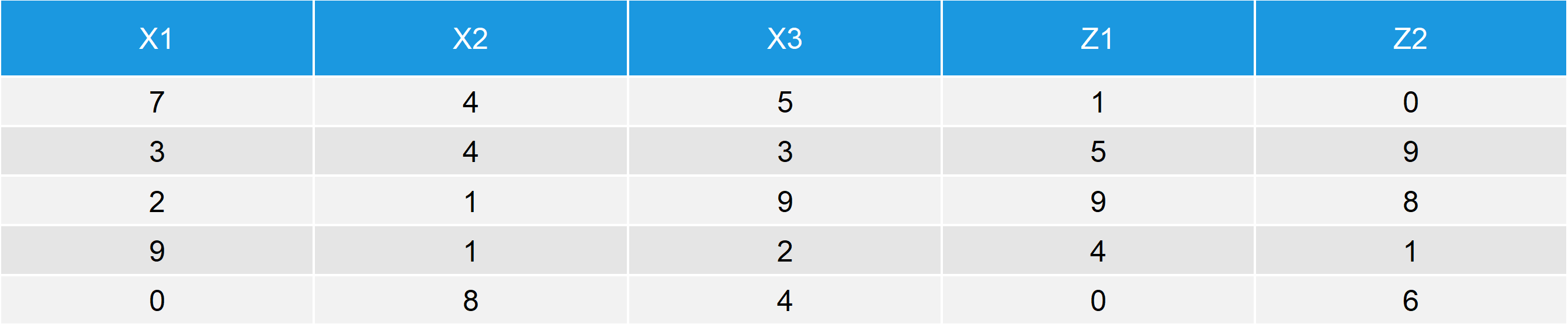
Table 2: Output after Using cbind for Two Data Frames.
Similar to Example 1, the first three columns consist of data_1 and the last two columns of the output consist of data_2.
Note: Both data frames have the same column length. The cbind R function cannot be used, in case that the number of rows of the two data frames differs.
Example 3: R cbind Multiple Columns
So far, we have applied cbind only in order to merge two data objects: In Example 1 to a data frame and a vector; in Example 2 to two data frames. However, the cbind function can also be applied to cbind multiple columns and data objects. For the following example, I’m using the data frame data_1; the vector Y1; and the data frame data_2 (created in the previous two examples):
data_new3 <- cbind(data_1, y1, data_2) # cbind two data frames and vector data_new3 # Print data to RStudio console
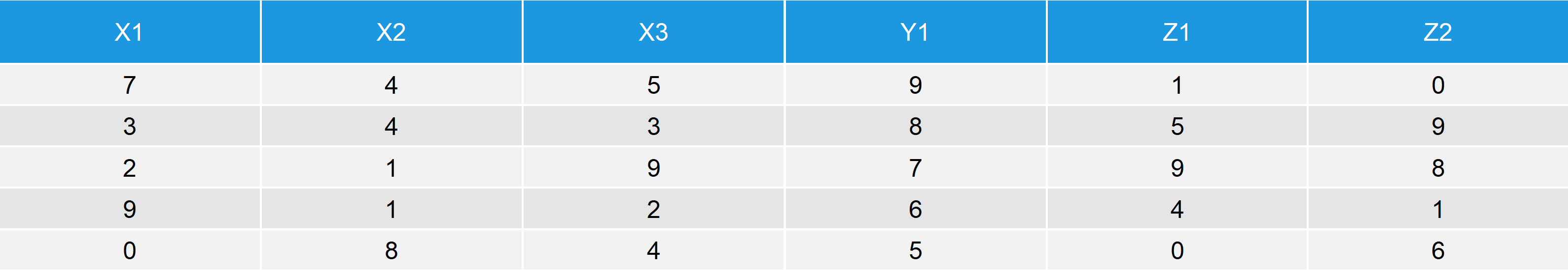
Table 3: Application of cbind to Multiple Columns in R.
The first 3 columns of data_new3 consist of data_1; the fourth column consists of the vector Y1; and the last two columns consist of data_2.
Exactly, as we wanted – perfect!
Video: cbind and rbind Explained
More explanations on how to copy multiple columns from one file to another using the cbind function needed? Then I can recommend the following video of my YouTube Channel. In the video, I’m explaining the R code of this tutorial in more detail.
Further Reading
- The rbind Function in R
- bind_rows & bind_cols functions of dplyr Package
- The merge Function in R
- Add New Column to Data Frame in R
- Convert List to Data Frame
- Subsetting Data Frame in R
- The nrow Function in R
- The R Programming Language







2 Comments. Leave new
Nice explanation!
Thanks a lot for the kind words, glad it was useful!