Create List of Installed Packages in R (Example)
In this article, I’ll explain how to get the names of all installed packages of a user in the R programming language.
The content of the page looks as follows:
Let’s jump right to the exemplifying R code:
Example: Return List of Installed Packages & Version Using installed.packages() Function
This example explains how to get the names of all installed add-on packages in R.
For this, we can use the installed.packages() function as shown below
my_packages <- as.data.frame(installed.packages()[ , c(1, 3:4)]) # Apply installed.packages() my_packages <- my_packages[is.na(my_packages$Priority), 1:2, drop = FALSE] # Keep NA rows rownames(my_packages) <- NULL # Rename rows head(my_packages) # First six packages
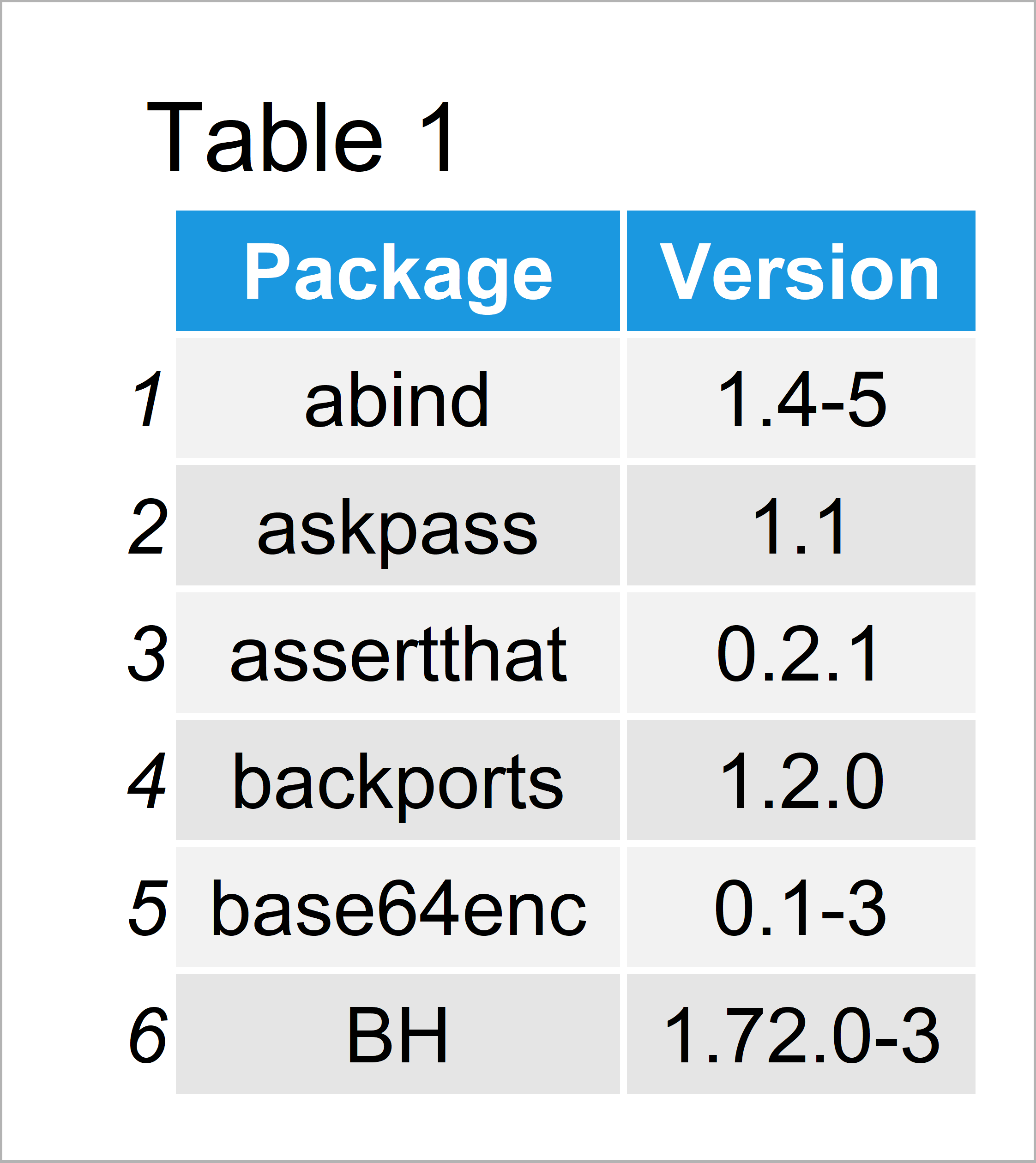
In Table 1 you can see that we have created a data frame containing all packages and versions of our installed packages.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
Would you like to know more about installed add-on packages? Then you may want to have a look at the following video of my YouTube channel. In the video, I’m explaining the R programming codes of this post:
In addition to the video, you may want to have a look at the other tutorials of this website. A selection of articles on topics such as directories and lists can be found below:
- List of Useful R Packages
- Get & Set Directory Path of Installed Packages Using libPaths Function
- Introduction to R
At this point you should have learned how to return a list of all installed add-on packages in R. In case you have additional questions and/or comments, let me know in the comments section below.






