Add Row to Empty Data Frame in R (Example)
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to append a new row to an empty data frame in R.
The table of content looks as follows:
With that, let’s jump right to the example:
Creating Example Data
The first step is to create some example data:
data <- data.frame(x1 = numeric(0), # Create empty data frame x2 = numeric(0), x3 = numeric(0)) data # Print empty data frame # [1] x1 x2 x3 # <0 rows> (or 0-length row.names)
As you can see based on the previous output of the RStudio console, we have created an empty data frame with zero rows in R.
Example: Adding New Row to Empty Data Frame Using Index Position
In this section, I’ll explain how to add new rows to our empty data frame.
For this, we can use the index position of our new row, i.e. the index position 1.
Consider the following R code:
data[1, ] <- 1:3 # Add new row to empty data data # Print updated data
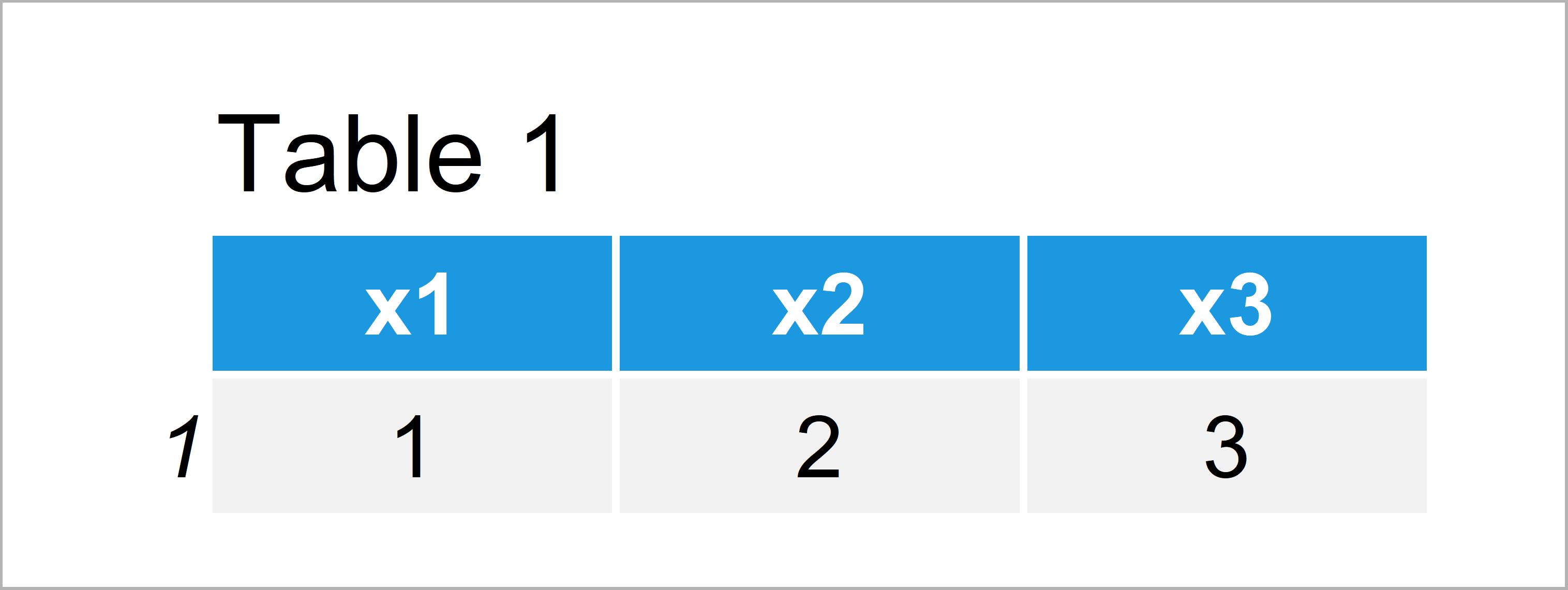
Table 1 shows the output of the previous syntax: A data frame with a header and one row.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
Have a look at the following video of my YouTube channel. In the video, I illustrate the R code of this article:
In addition, you may want to read some of the other tutorials of my website. Please find some tutorials on related topics such as loops and indices below:
- Append to Data Frame in Loop
- Add New Row to Data Frame in R
- Add New Row at Specific Index Position to Data Frame
- Introduction to R
At this point you should know how to add new rows to empty data frames with a header in R programming. If you have further questions, please let me know in the comments section. In addition, don’t forget to subscribe to my email newsletter in order to get updates on the newest tutorials.






