Sample Random Rows of Data Frame in R (2 Examples) | Select with Base R vs. dplyr Package
This tutorial illustrates how to select random rows in a data frame in the R programming language.
The article will consist of the following information:
- Construction of Example Data
- Example 1: Sample Random Rows of Data Frame with Base R
- Example 2: Sample Random Rows of Data Frame with dplyr Package
- Video & Further Resources
So without further ado, here’s the step-by-step process.
Construction of Example Data
In the examples of this tutorial, I’ll use the following data frame:
data <- data.frame(x1 = 1:5, # Create example data x2 = LETTERS[1:5], x3 = c(4, 1, 9, 0, 1)) data # Print example data
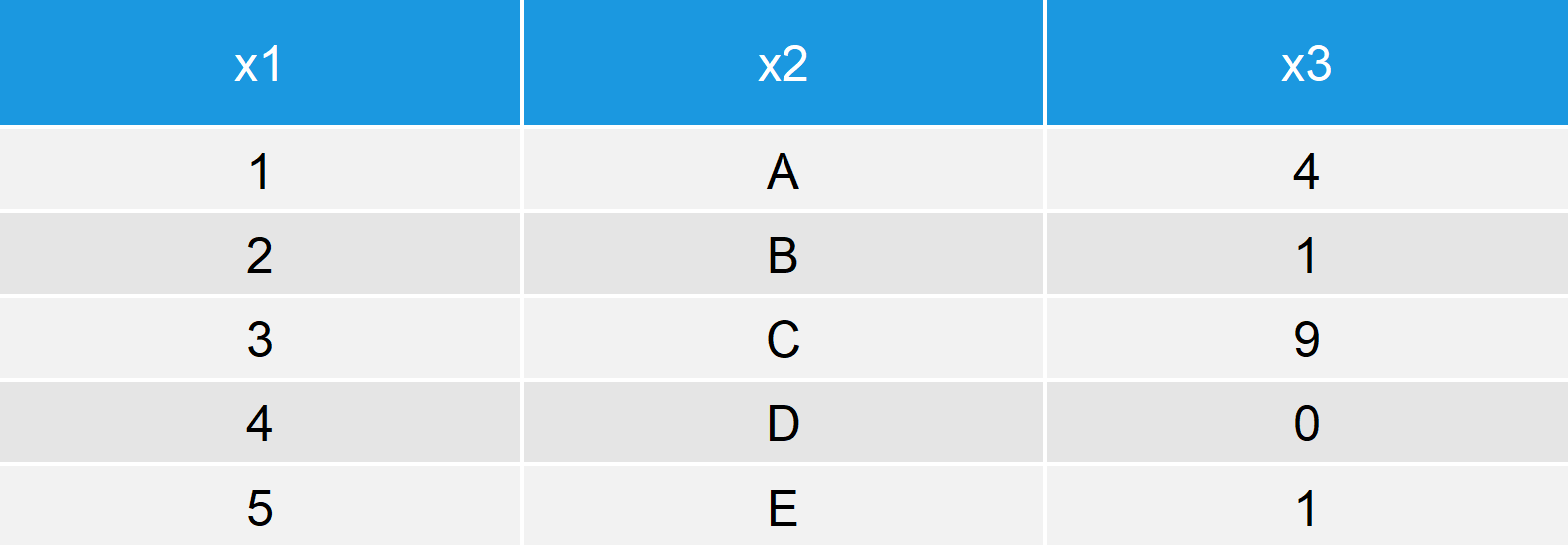
Table 1: Example Data Frame in R Programming Language.
Our data frame contains three columns and five rows. In the following, I’ll show you how to sample some rows of this data frame randomly.
Example 1: Sample Random Rows of Data Frame with Base R
First, let’s set a seed so that we are able to reproduce this example afterwards:
set.seed(12345) # Set seed for reproducibility
Now, we can draw a random sample of our data frame with the sample R function as follows:
data_s1 <- data[sample(1:nrow(data), 3), ] # Sample rows of data with Base R data_s1 # Print sampled data
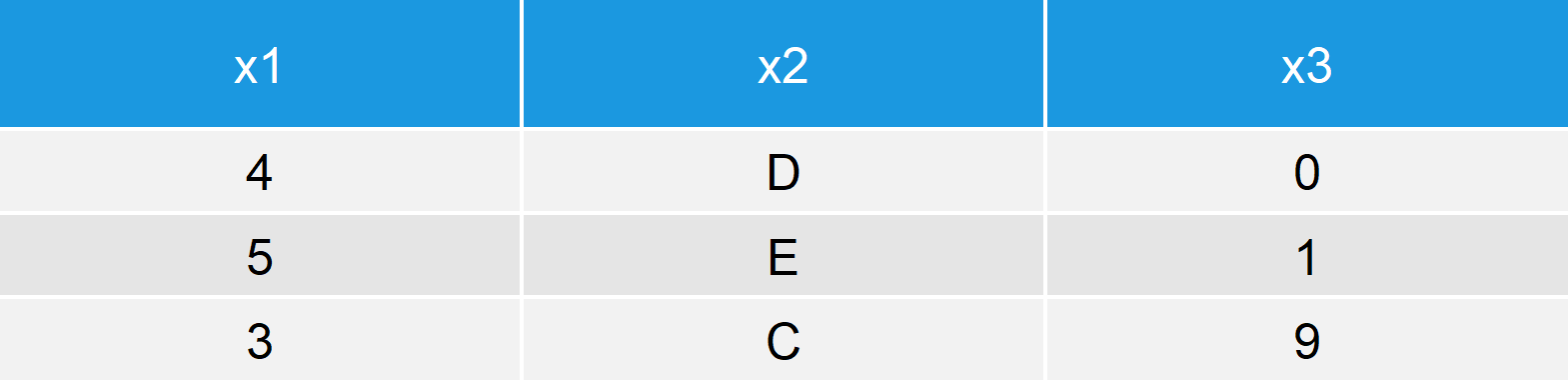
Table 2: Sampled Data Frame by Rows in R Programming Language.
As you can see based on Table 2, our sampled data matrix contains three rows (i.e. two rows were removed).
You can read the previous code as follows:
- With data_s1 <- we specify that we want to store the sampled data in the data object data_s1.
- With [ … , ] we specify that we want to take a subset of the rows of our data.
- With sample( … ) we specify that we want to use the sample function of Base R.
- With 1:nrow(data), 3 we specify that we want to select three random values between 1 and the number of rows of our data frame.
That’s the solution, which is already provided with the base installation of R (or RStudio). However, some people prefer to use the dplyr package for data manipulation. I’m therefore going to show you next, how to take a subsample based on the dplyr environment.
Example 2: Sample Random Rows of Data Frame with dplyr Package
Before we can extract a subset based on the dplyr environment, we need to install and load the dplyr package in R:
install.packages("dplyr") # Install dplyr package library("dplyr") # Load dplyr package
Let’s also set a seed in order to provide reproducibility of our example:
set.seed(12345) # Set seed for reproducibility
Now, we can apply the sample_n function of the dplyr package to take a sample of our example data frame:
data_s2 <- sample_n(data, 3) # Sample rows of data with dplyr data_s2 # Print sampled data
The output is exactly the same as in Example 1, as you can see in your RStudio console by running the previous R code.
Video & Further Resources
I have recently published a video on my YouTube channel, which explains the contents of this tutorial. You can find the video below:
Furthermore, you might want to read the other posts on https://statisticsglobe.com/.
- sample Function in R
- sample_n & sample_frac R Functions of dplyr Package
- Subset Data Frame Rows by Logical Condition
- Extract Certain Columns of Data Frame in R
- R Functions List (+ Examples)
- The R Programming Language
In this R tutorial you learned how to extract rows from a data.frame randomly via simple random sampling. Let me know in the comments, if you have additional comments or questions on the subsetting of data frames. In addition, don’t forget to subscribe to my email newsletter to receive updates on new tutorials.