Delete Duplicate Rows Based On Column Values in R (Example)
In this article, I’ll demonstrate how to extract unique rows based on a logical condition in R.
The content of the page is structured as follows:
So without further additions, let’s just jump right in!
Creation of Exemplifying Data
The first step is to define some data that we can use in the examples below:
data <- data.frame(x = c("a", "a", "a", "a", "b", "b", "c"), # Create example data y = c(3, 1, 4, 2, 1, 2, 1)) data # Print example data
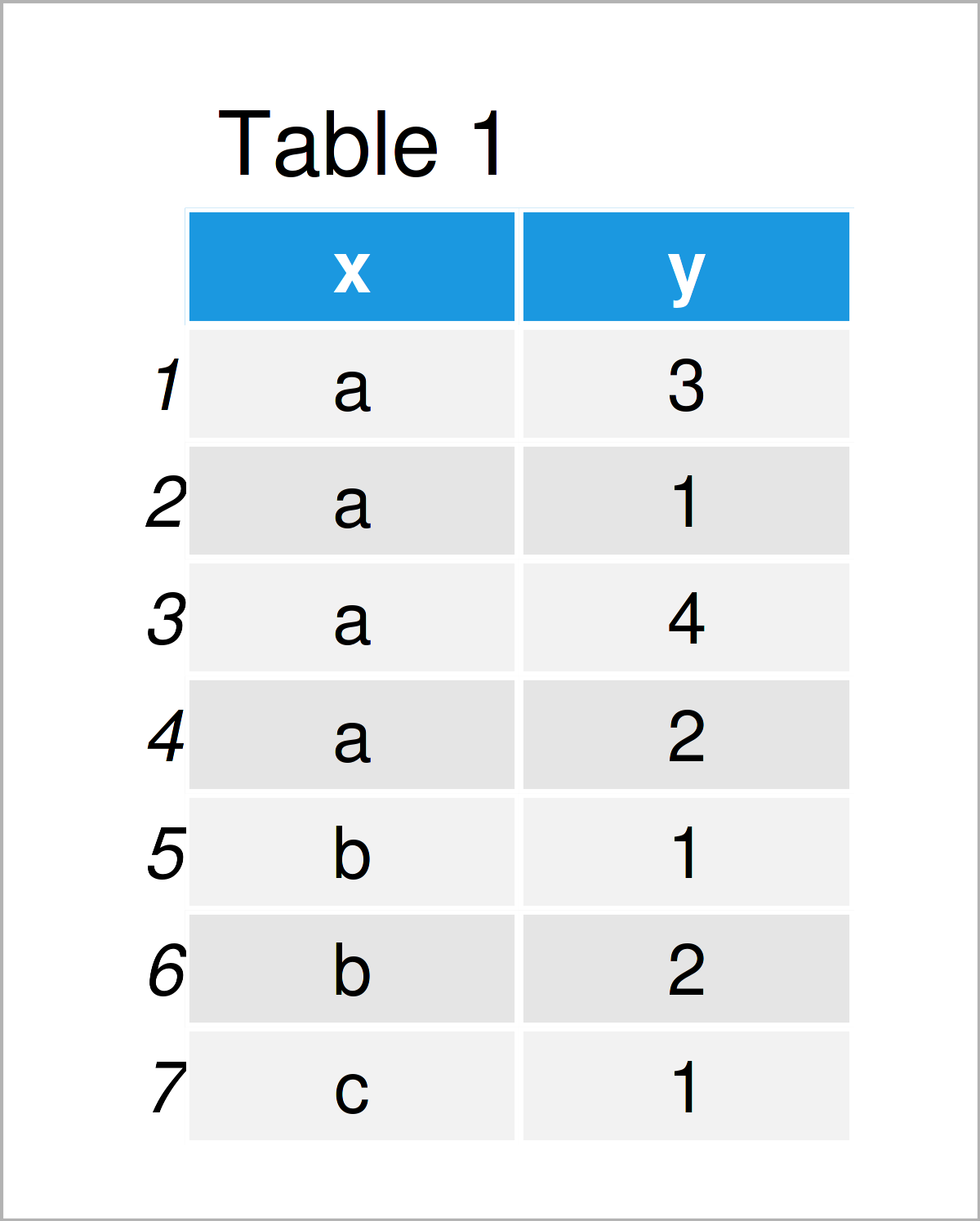
Table 1 illustrates the output of the RStudio console that got returned after executing the previous R syntax and shows that our example data has seven data points and two columns called “x” and “y”.
As you can see, the variable x contains several duplicates. We may remove the duplicates from our data as shown below:
data_default <- data[!duplicated(data$x), ] # Extract unique rows data_default # Print data with unique rows
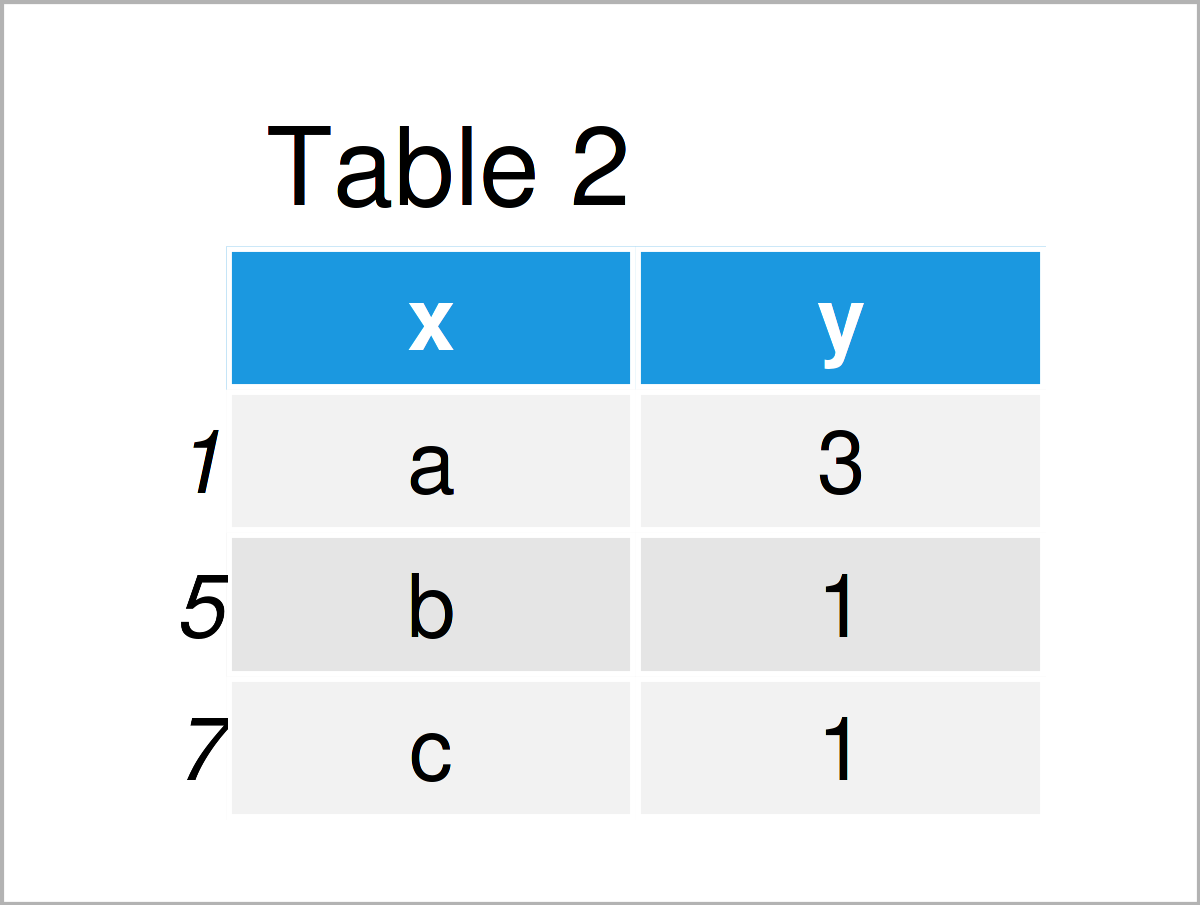
As shown in Table 2, the previous code has created a data set containing each value in the column x only once.
However, you can also see that we have returned the first row of each value in x. In the following example, I’ll explain how to extract rows conditionally based on another column.
Example: Subset of Unique Rows with Highest Values in Column
The following R programming syntax explains how to return the highest value in y for each duplicate in x.
To do this, we first have to order our data set in decreasing order according to the column y:
data_ordered <- data[order(data$y, decreasing = TRUE), ] # Order data data_ordered # Print ordered data
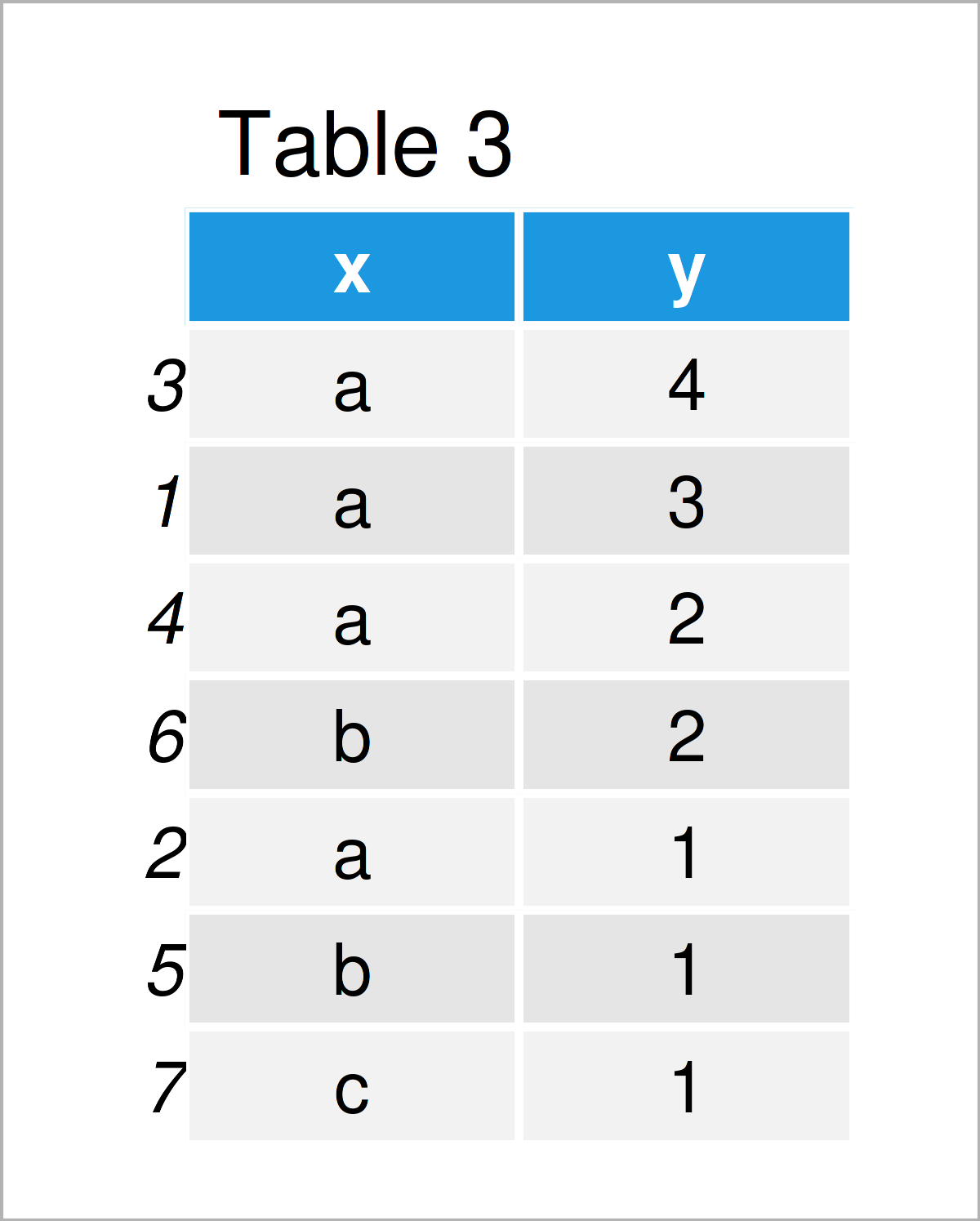
The output of the previous R code is shown in Table 3 – A data frame sorted according to the variable y.
In the next step, we can delete all duplicates from our data:
data_highest <- data_ordered[!duplicated(data_ordered$x), ] # Unique rows of ordered data data_highest # Print unique rows of ordered data
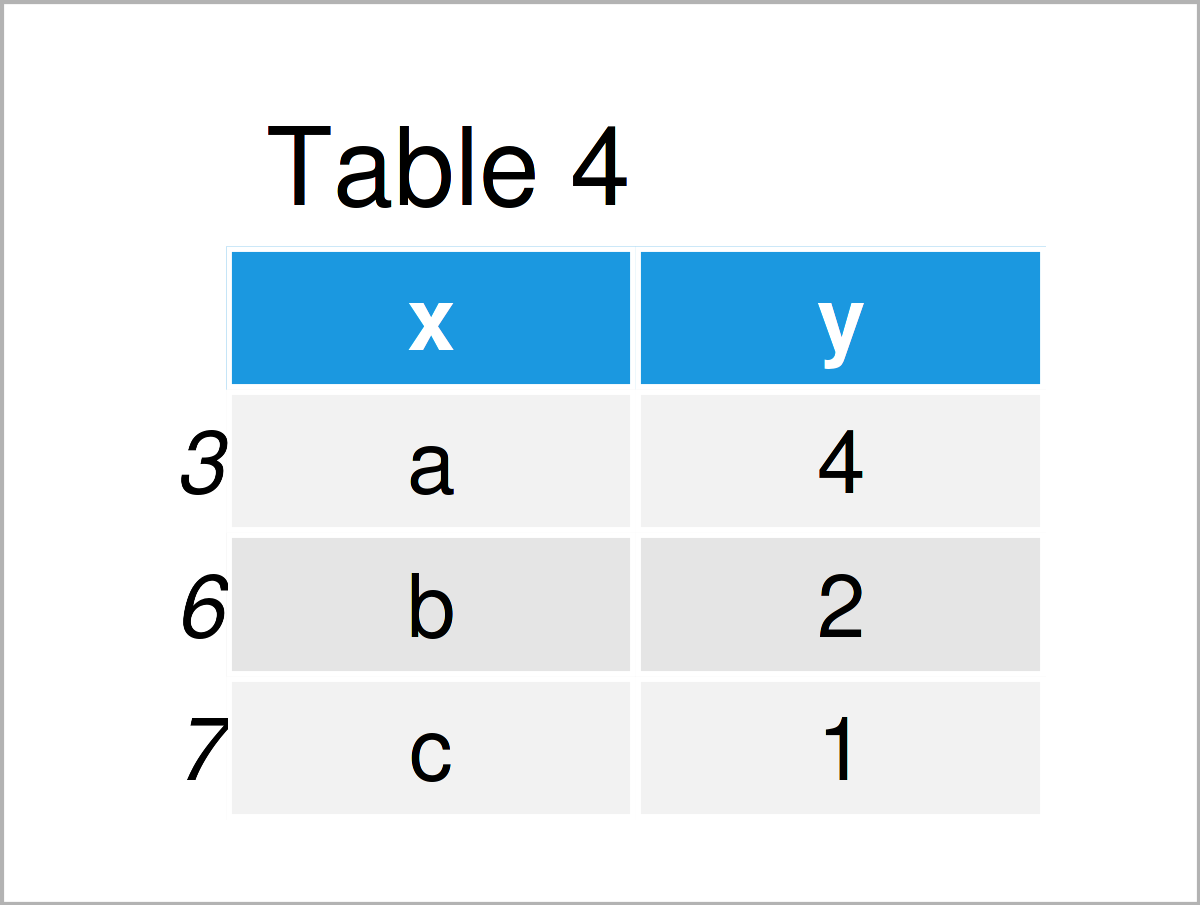
Table 4 shows the output of the previous R syntax: A data frame subset with unique elements in x and the highest corresponding values in y.
Video, Further Resources & Summary
I have recently published a video on my YouTube channel, which demonstrates the R programming codes of this tutorial. Please find the video below.
Furthermore, you may read the other articles that I have published on this homepage.
- Select Data Frame Rows where Column Values are in Range
- Select Data Frame Rows based on Values in Vector
- R Programming Tutorials
In this R tutorial you have learned how to select unique rows based on a logical condition. Don’t hesitate to let me know in the comments section, in case you have additional questions.